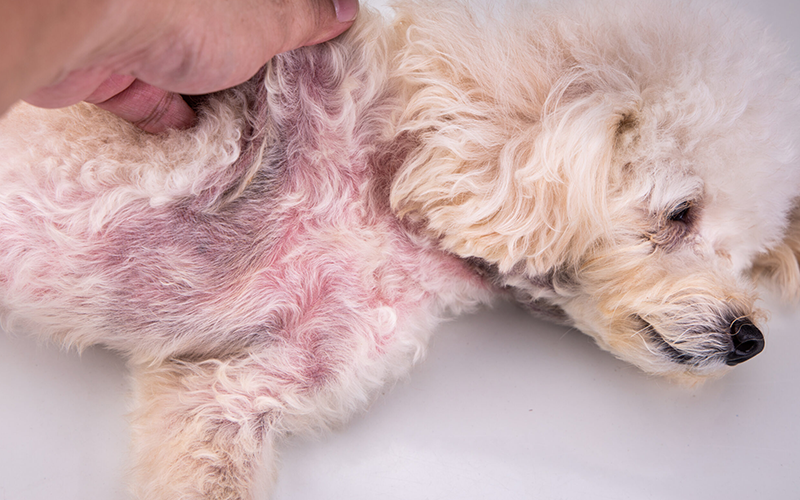
Red Patches on Your Dog’s Skin: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
Introduction
If you’ve noticed red patches on your dog’s skin, you’re not alone. Many dog owners face this concern at some point in their pet’s life. Red patches can be a sign of various conditions, from minor skin irritation to more serious underlying health problems.
Understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial to ensuring your furry friend’s comfort and overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the potential reasons behind red patches on dog skin, how to treat them, and effective
prevention methods. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to care for your dog’s skin and keep them healthy and happy.
Common Causes of Red Patches on Dog Skin
-
Allergies (Environmental or Food-related)
One of the most common causes of red patches on a dog’s skin is an allergic reaction. Dogs can develop allergies to environmental triggers like pollen, mold, dust mites, or chemicals
in household cleaning products. Food allergies are also prevalent and can lead to redness, itching, and inflammation. Common allergens include proteins like chicken, beef, dairy, or grains like wheat.Symptoms of allergies in dogs include:
- Red or inflamed skin
- Itching and scratching
- Hair loss in affected areas
- Ear infections or watery eyes
- Vomiting or diarrhea (in the case of food allergies)
Treatment for allergies:
- Identifying the allergen: An elimination diet or allergy testing by a veterinarian can help identify food allergens.
- Medications: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or allergy shots may be prescribed by a veterinarian.
- Environmental management: Reduce exposure to allergens by keeping your home clean, using air purifiers, and washing your dog’s bedding regularly.
-
Fleas and Other Parasites
Fleas are a common cause of skin irritation in dogs, leading to the development of red patches, especially in areas where fleas bite, such as the abdomen, groin, and around the tail. Flea bites can
cause itching, redness, and sometimes secondary infections from scratching. Other parasites, like ticks, mites, or lice, can also cause similar symptoms.Symptoms of flea infestations include:
- Red, inflamed skin
- Excessive scratching or biting
- Hair loss in localized areas
- Scabs or crusts on the skin
- Presence of fleas or flea dirt (tiny black specks) on your dog’s coat
Treatment for flea infestations:
- Flea medications: Use flea preventatives, such as topical treatments, oral medications, or flea collars.
- Environmental cleaning: Vacuum your home regularly, wash your dog’s bedding, and treat your home with flea sprays or foggers if needed.
- Bathing: Bathe your dog with a flea shampoo to help eliminate fleas and soothe irritated skin.
-
Hot Spots (Acute Moist Dermatitis)
Hot spots are localized, inflamed areas of the skin that often become infected due to excessive moisture, bacteria, or scratching. They commonly occur in areas like the face, neck, or hips.
Hot spots can develop quickly and become very painful for your dog.Symptoms of hot spots include:
- Red, oozing, or crusted patches of skin
- Intense itching and discomfort
- Hair loss around the affected area
- A foul odor emanating from the lesion
Treatment for hot spots:
- Veterinary care: In severe cases, hot spots may require a vet visit for antibiotics or corticosteroids.
- Prevent scratching: Use an Elizabethan collar (cone) to prevent your dog from further irritating the area.
- Topical treatments: Your veterinarian may recommend antiseptic solutions, hydrocortisone sprays, or other topical treatments to reduce inflammation and infection.
-
Yeast Infections (Malassezia Dermatitis)
Yeast infections, specifically Malassezia dermatitis, are another potential cause of red, inflamed patches on your dog’s skin. Yeast naturally lives on your dog’s skin, but when there
is an overgrowth due to certain factors like allergies, a weakened immune system, or moist conditions, it can lead to redness, itching, and scaling.Symptoms of yeast infections include:
- Red, greasy, or scaly patches
- A strong, musty odor
- Itching or discomfort
- Darkened skin (hyperpigmentation) in chronic cases
- Ear infections or inflamed paws
Treatment for yeast infections:
- Antifungal medications: Your veterinarian may prescribe topical antifungals or oral medications to combat the infection.
- Regular bathing: Bathe your dog with a gentle, medicated shampoo designed for yeast infections to reduce the growth of yeast.
- Address underlying issues: Treat any underlying health problems like allergies or hormonal imbalances that could be contributing to the infection.
-
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections, often resulting from cuts, abrasions, or excessive scratching, can cause red, inflamed patches of skin. These infections are usually marked by swelling, pus, and increased warmth around
the infected area. In some cases, secondary infections may occur due to a compromised immune system or other health issues.Symptoms of bacterial infections include:
- Red, swollen patches of skin
- Presence of pus or crusting
- Increased warmth or tenderness around the affected area
- Hair loss or matting in the infected region
- Foul odor emanating from the skin
Treatment for bacterial infections:
- Antibiotics: Your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics or topical ointments to treat the infection.
- Wound care: Clean the affected area with a gentle antiseptic and avoid further irritation.
- E-collar: An Elizabethan collar may be necessary to prevent your dog from scratching or licking the infected area.
-
Fungal Infections (Ringworm)
Ringworm is a highly contagious fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. It can cause round, red patches of hair loss, typically with a scaly border. Although it’s called “ringworm,”
it’s not actually a worm but a fungal infection.Symptoms of ringworm include:
- Circular patches of hair loss with a red, raised border
- Scaly, flaky skin
- Itching or discomfort
- Red or inflamed areas around the ringworm patch
- Crusty lesions
Treatment for ringworm:
- Antifungal treatment: Your vet may recommend topical or oral antifungal medications to treat the infection.
- Environmental cleaning: Since ringworm is highly contagious, cleaning your home and disinfecting surfaces is crucial to prevent the spread of the infection.
-
Dermatitis and Skin Inflammation
Dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin, which can result from a variety of causes, including allergies, infections, or irritants. The inflammation can manifest as red patches, scabs,
or blisters on the skin, often accompanied by itching and discomfort.Symptoms of dermatitis include:
- Red, inflamed patches of skin
- Scabs, blisters, or sores
- Intense itching
- Hair loss in the affected areas
- Thickened or leathery skin in chronic cases
Treatment for dermatitis:
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antibiotics or antifungals: Depending on whether the dermatitis is bacterial or fungal.
- Avoid irritants: Try to identify and eliminate the cause of the dermatitis, such as certain grooming products or environmental allergens.
When to See a Veterinarian
While minor skin irritations may resolve with proper care and treatment, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian if:
- The red patches are persistent or worsen over time.
- Your dog is experiencing significant discomfort, excessive scratching, or hair loss.
- You notice signs of infection, such as pus, swelling, or foul odor.
- There is no improvement after basic treatments like flea control or bathing.
- Your dog’s overall behavior or health seems affected.
A veterinarian will be able to conduct a thorough examination, perform necessary tests (like skin scrapings, allergy testing, or cultures), and determine the best course of treatment.
Prevention Tips for Healthy Dog Skin
- Regular grooming: Keep your dog’s coat clean and free of mats to prevent skin irritations. Regular baths with gentle dog shampoos can help remove allergens and dirt that might cause inflammation.
- Flea prevention: Use flea preventatives year-round to minimize the risk of flea infestations and the itching and irritation they cause.
- Healthy diet: A balanced, high-quality diet that meets all of your dog’s nutritional needs can help maintain skin health and reduce the likelihood of food allergies or deficiencies.
- Moisturizing your dog’s skin: Dry, flaky skin can lead to irritation and inflammation. Use pet-safe moisturizers or oils to help keep their skin hydrated.
- Monitor your dog’s health: Regular vet checkups can catch skin issues early and help manage underlying health conditions that may contribute to skin problems.
Conclusion
Red patches on your dog’s skin can be a sign of several different conditions, ranging from simple allergies to more complex infections or parasites. Identifying the cause early and seeking appropriate treatment is key to ensuring your dog remains comfortable
and healthy. By following the treatment and prevention
共输入 10640 字符
清除文字效果







